Starting your journey into the online world can feel like a crazy place where the inhabitants speak a totally new language.
So here’s a glossary of commonly used terms we’ve created to help you!
Avatar
![]() An avatar is a computer user’s online representation of themself or their alter ego.
An avatar is a computer user’s online representation of themself or their alter ego.
Your avatar is an important part of your online identity.
It’s an online representation of you that shows up in places such as where you leave comments, forum posts or on social networks and is part of how others visualize who you are.
For more information refer to:
- Creating And Uploading Your Comment Avatar
- Want A Comment Avatar That’s Globally Recognised By Most Blog Platforms? Here’s How!
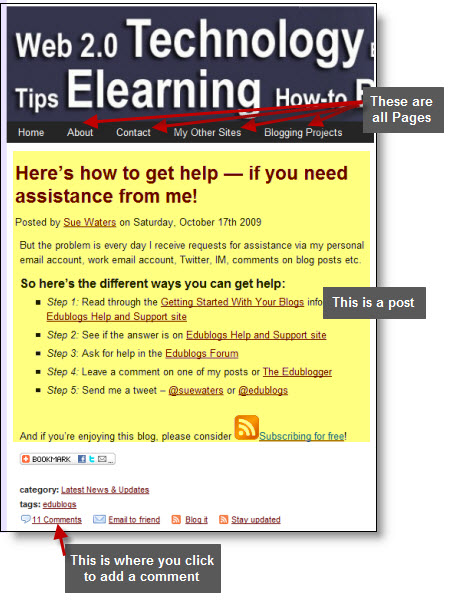
Blog
The term blog originated from the blend of the term “web log”.
Blogs are normally made up of the following main elements:
- Posts – Posts are where you normally publish the latest new or new article on a blog. They are commonly displayed in reverse-chronological order with the most recent post at the top of the page. Blogs are designed to have only one Post page.
- Comments – Posts commonly allow readers to publish comments on the posts they read. This is where the reader can share their thoughts, connect with the blogger and interact with other readers.
- Pages – You normally use pages for information that you want to share with your readers but don’t expect to update frequently. Not all blogging software includes the ability to add Pages.
Blogs are written on just about any subject and for a wide range of purposes, including personal, business, work and sharing news stories.
Here’s some examples of how blogs are used and educational blogs to check out:
- Top ten ways educators use blogs with students
- Class blogs:
- MrToft.ca (Grade 5)
- Huzzah (Grade 6/7)
- Blog, blog blog blog, blog some more (English I)
- Student blogs:
- Jazzing up Eight Grade
- Lauren’s Life
- Dominique’s My Blog
- Education blogs listed on PostRank
Cloud Computing
In really simple terms, cloud computing involves using off-site providers that you access via the Internet, and paying for what you use as it’s needed, instead of managing aspects such as hardware, computer applications and data storage on-site.
The term “cloud” is used as a metaphor for the Internet.
Examples of cloud computing include using:
- Google Apps for purposes such as email, messaging, documents, spreadsheets, calendar
- Skype for free online calls, messaging, video conferencing, applicaton sharing, file sharing
- Facebook as a free Intranet
Watch Cloud Computing in Plain English for more information.
Personal Learning Network (PLN)
 Personal Learning Networks (PLNs) are all about using web tools such as blogs, wiki, twitter, facebook to create connection with others which extend our learning, increases our reflection while enabling us to learn together as part of a global community.
Personal Learning Networks (PLNs) are all about using web tools such as blogs, wiki, twitter, facebook to create connection with others which extend our learning, increases our reflection while enabling us to learn together as part of a global community.
PLNs increase our opportunities to ask questions and receive help compared to our normal daily face-to-face interactions.
Best part of a PLN is it’s personal!
You make all the choices:
- What tools you use!
- Who you connect with!
- How you want to learn!
- When you want to learn!
Terms like Personal Learning Communities (PLC) and Personal Learning Environments (PLE) are occassoinally used in a similar context to Personal Learning Networks (PLN).
Check out PLN Yourself to learn more about building your own PLN.
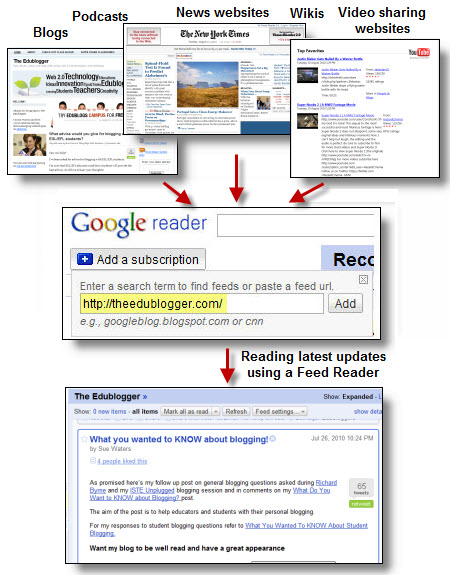
RSS
RSS is an acronym which stands for Really Simple Syndication.
In simple terms, RSS is a simple and effective way of keeping in touch when new information is added to a website without having to visit the website to check for new updates.
How it works is you subscribe to your favorite website using the RSS feed in a RSS feed reader such as Google Reader. Whenever new information is added to the website it is automatically sent to your RSS feed reader where you can read it at your convenience.
For example, whenever your favorite blogger publishes a new post it is automatically sent to your Feed reader.
![]() Sites with RSS feeds are normally indicated with the word RSS and/or the orange RSS icon.
Sites with RSS feeds are normally indicated with the word RSS and/or the orange RSS icon.
For more information:
- Watch RSS in Plain English
- Follow these instructions to subscribe to blogs using Google Reader — just replace the student blogs with your favorite blogs and news services
Please note :
- Blogs on all standard blogging platforms automatically include RSS feeds and don’t necessarily use words or an icon to indicate the presence of the RSS feed
- RSS lets you do lots of cool stuff including adding latest updates from your favorite blog(s) or news website(s) to your own site using RSS widgets like FeedWind’s RSS widget
Social Bookmarking
Social bookmarking enables people to bookmark and tag online content such as websites they find useful so they can use for future reference or share with others online.
Using social bookmarking sites such as Delicious and Diigo means that you can access your stored references anywhere, anytime on any computer.
Social Networking
Social networking is the act of communicating and building relationships with people online.
Blogs, Twitter, Facebook, Ning communities, LinkedIn, Flickr are all examples of popular social networking sites used by educators to develop their Personal Learning Network (PLN).

Tag
Tags are keywords or terms used to classify content and organize content stored online. Tags are commonly assigned informally by person who creates the content.
The purpose of tagging is to help make it easier for the content to be easily found. Tagging is an important part of many web 2.0 tools including:
- Blog posts
- Images stored on photosharing websites such as Flickr
- Bookmarks stored on social bookmarking sites such as Delicious and Diigo
You’ll often see tag clouds used as a visual representation of tags used on a website. The larger the size of the word in the tag cloud the more content has been tagged using that term.
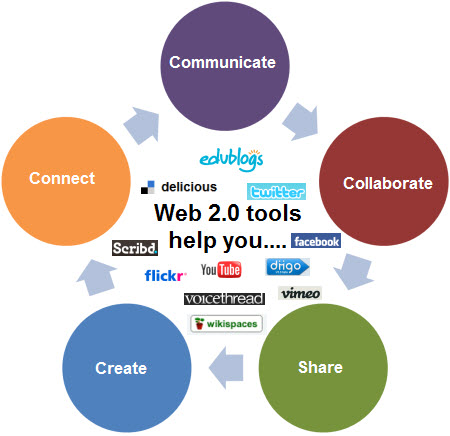
Web 2.0
The term “Web 2.0” begun its rise into popularity when O’Reilly Media and MediaLive hosted the first Web 2.0 conference in 2004.
It’s used to refer to the supposed second-generation of Internet-based services that let people collaborate and share information online in new ways.
Blogs, wikis, podcasting, video sharing websites (e.g. YouTube and Vimeo), photosharing websites (e.g. Flickr and Picasa), social networking sites (e.g. FaceBook, Twitter) are all examples of Web 2.0 technologies.
The phrase “Web 2.0” hints at an improved form of the World Wide Web.
The early web development, retrospectively now labelled Web 1.0, involved static websites, the use of search engines, and surfing from one website to the next, and consuming of consumer created by geeks and web coder.
Web 2.0 involves a more dynamic and interactive World Wide Web where anyone can create content and connect with others to collaborate to build on each others content.
Wiki
A wiki is a website that allows easy creation and editing of webpages using your web browser. Wikis are normally powered by wiki software.
The term wiki is derived from the Hawaain word ‘fast’ because non-technical users can use them quickly and easily to create their own websites.
Wikipedia is the best example of a wiki being used colloboratively by a community to create content.
Commonly used wikis providers chosen by educators include Wikispaces, Wetpaint, and PBWorks.
FINAL THOUGHTS
Thanks to everyone in my Twitter network who provided input into which terms should be included in this glossary and for sharing links to references.
There is a good chance that in attempting to keep the explanations short we haven’t covered them in sufficient details. So would love to hear your thoughts:
- What terms need better explaining? Or explained differently?
- What other terms would you like included?
If you are enjoying reading this blog, please consider ![]() Subscribing For Free!
Subscribing For Free!
Hi Sue, thanks for the time invested in your research. This keeps us in a know of the new technology terms development.
Thanks